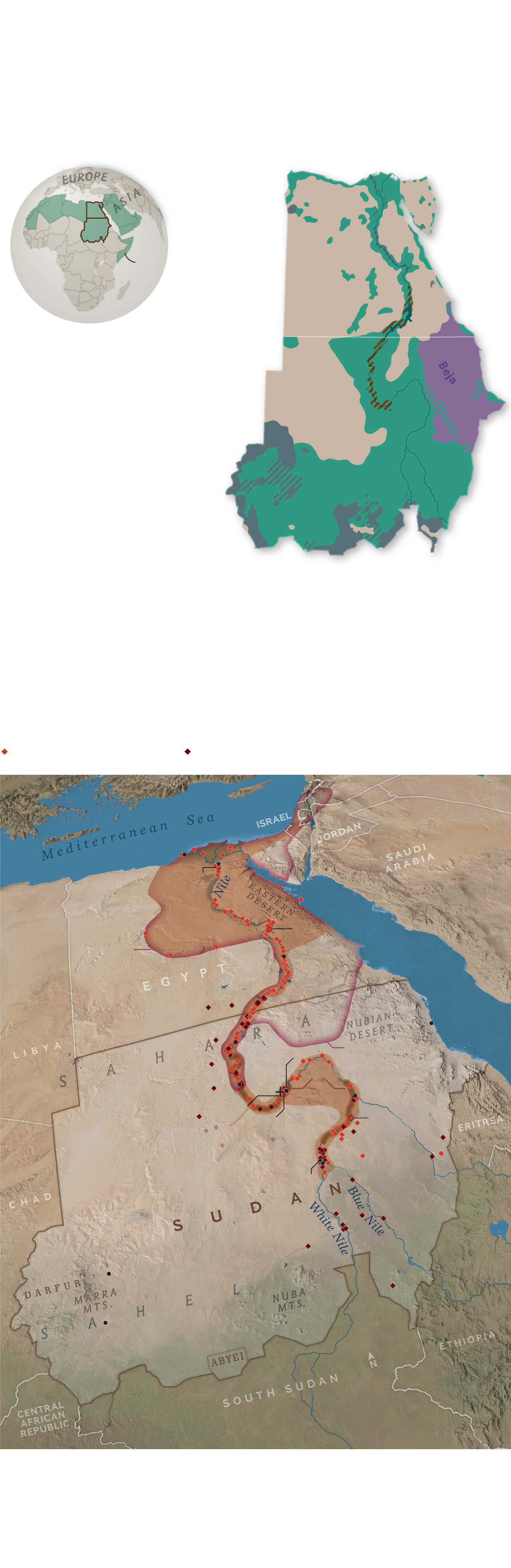
Shaping the future
Arab nationalism and Islamism have molded much of Sudan’s political present,
particularly in the country’s arid north. But many Sudanese are turning to
three millennia of cultural history to build a new identity—one that balances
ancient African heritage with recent centuries of Arab influence.
Sudan is one of 10 African nations that are members of the Arab League.
EGYPT
Arabs
SAHARA
SUDAN
AFRICA
EGYPT
Arab League
member states
A diverse mix
Nubians
Arabic spread into the region with the rise of Islam in the seventh century, but Sudan is still home to more than 500 ethnic groups and over 400 languages. Most ethnic Nubians are concentrated in small pockets and primarily speak Arabic; there are efforts to revive the Nubian language. The nomadic Beja speak their ancient language, Beja.
Others
SUDAN
Arabs
Powerful past
The Nubian kings of the Kushite Empire, once a vassal of Egypt, gradually
conquered their foreign ruler beginning in 750 B.C., reviving Egypt’s art
and architecture and prevailing in Egypt for nearly a century. Major trading
centers in the Kushite heartland in the Nile Valley linked African,
Mediterranean, and Near Eastern cultures.
Archaeological sites
3000 B.C. to A.D. 1400
Before 3000 B.C.
Alexandria
Cairo
LOWER
EGYPT
LOWER
EGYPT
Memphis
Kushite capital of Egypt,
7th century B.C.
Red
Sea
UPPER
EGYPT
UPPER
EGYPT
Under
Kushite rule
(ca 750–656 B.C.)
Thebes
Major Egyptian and Kushite
religious center
Area of Egyptian
dominance
(ca 1550–770 B.C.)
Aswan
Boundary
claimed
by Sudan
Lake
Nasser
LOWER
NUBIA
LOWER
NUBIA
Abu Simbel
Wadi Halfa
Port Sudan
Area of Egyptian
dominance
Area of Egyptian
dominance
Nuri
UPPER
NUBIA
Kushite Heartland
Jabal
Barkal
Dongola
Atbara
Karima
Ed
Damer
El Kurru
Meroë
Major
Kushite
city
Napata
Early Kushite capital and religious
center at the base of Jabal Barkal,
late 7th century B.C.
Kassala
Khartoum
Omdurman
Wad Medani
Rabak
Grand
Ethiopian
Renaissance
Dam
El Fasher
Nyala
Boundary
claimed by
South Sudan
Scale varies in this perspective. Distance from Khartoum
to Cairo is approximately 1,000 miles.
Christine Fellenz, Matthew W. Chwastyk, and Patricia Healy, NGM Staff.
Sources: Ancient Nubia: African Kingdoms on the Nile, Marjorie Fisher (editor)
and Thomas James (maps); Michael Izady, Atlas of the Islamic World and
Vicinity; Peter Lacovara, Ancient Egyptian Heritage and Archaeology Fund;
Geoff Emberling, University of Michigan; Derek Welsby
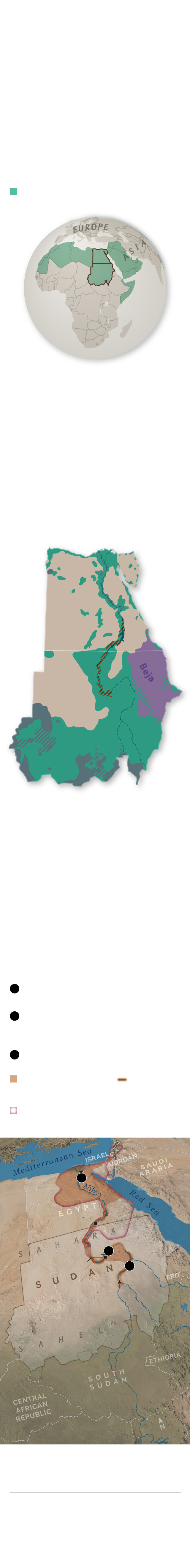
Shaping the future
Arab nationalism and Islamism have
molded much of Sudan’s political
present, particularly in the country’s
arid north. But many Sudanese are
turning to three millennia of cultural
history to build a new identity—
one that balances ancient African
heritage with recent centuries of
Arab influence.
Sudan is one of 10 African nations that
are members of the Arab League.
Arab League member states
EGYPT
SAHARA
SUDAN
AFRICA
A diverse mix
Arabic spread into the region with
the rise of Islam in the seventh
century, but Sudan is still home to
more than 500 ethnic groups and
over 400 languages. Most ethnic
Nubians are concentrated in small
pockets and primarily speak Arabic;
there are efforts to revive the Nubian
language. The nomadic Beja speak
their ancient language, Beja.
Arabs
EGYPT
Nubians
Others
SUDAN
Arabs
Powerful past
The Nubian kings of the Kushite
Empire, once a vassal of Egypt,
gradually conquered their foreign
ruler beginning in 750 B.C., reviving
Egypt’s art and architecture and
prevailing in Egypt for nearly a
century. Major trading centers in the
Kushite heartland in the Nile Valley
linked African, Mediterranean, and
Near Eastern cultures.
Important archaeological sites
Kushite capital of Egypt,
7th century B.C.
1
Early Kushite capital and religious
center at the base of Jabal Barkal,
late 7th century B.C.
2
Major Kushite city
3
Under Kushite rule
(ca 750–656 B.C.)
Kushite
heartland
Area of Egyptian dominance
(ca 1550–770 B.C.)
Alexandria
Cairo
LOWER
EGYPT
LOWER
EGYPT
Memphis
Kushite capital
of Egypt,
7th century B.C.
1
Memphis
UPPER
EGYPT
UPPER
EGYPT
Under
Kushite rule
(ca 750–656 B.C.)
Under
Kushite rule
(ca 750–656 B.C.)
Thebes
Major Egyptian
and Kushite
religious center
Aswan
Lake
Nasser
Boundary
claimed
by Sudan
Boundary
claimed
by Sudan
Area of Egyptian
dominance
(ca 1550–770 B.C.)
Area of Egyptian
dominance
(ca 1550–770 B.C.)
LOWER
NUBIA
Abu Simbel
Wadi Halfa
Port Sudan
Meroë
Major
Kushite
city
Area of
Egyptian
dominance
Area of
Egyptian
dominance
Nuri
UPPER
NUBIA
Napata
Jabal Barkal
Karima
2
Dongola
Kushite
Heartland
Atbara
Jabal Barkal
El Kurru
Ed
Damer
Ed
Damer
3
Meroë
Kassala
Boundary
claimed
by Sudan
Boundary
claimed
by Sudan
Napata
Early Kushite capital
and religious center at
the base of Jabal Barkal,
late 7th century B.C.
Khartoum
Omdurman
Wad Medani
Wad Medani
Grand
Ethiopian
Renaissance
Dam
El Fasher
Nyala
Boundary claimed
by South Sudan
Boundary claimed
by South Sudan
Scale varies in this perspective.
Distance from Khartoum to Cairo
is approximately 1,000 miles.
Christine Fellenz, Matthew W.
Chwastyk, and Patricia Healy, NGM Staff.
Sources: Michael Izady, Atlas of the
Islamic World and Vicinity; Peter
Lacovara, Ancient Egyptian Heritage
and Archaeology Fund; Geoff Emberling,
University of Michigan; Derek Welsby